The Broad Impact of Stress Combination
Abiotic stresses such as drought, heat or flooding can have a devastating economical and sociological impact. Recent studies have linked the frequency of occurrences of severe abiotic stress events with global warming, underlining the urgent need to develop plants and crops with enhanced tolerance to abiotic stresses. These are expected to prevent annual losses of billions of dollars to agricultural production worldwide, as well as to decrease the impact of a potentially catastrophic future weather event(s). Drought and heat stress represent an excellent example of two different abiotic stress conditions that occur in nature simultaneously (Fig. 2).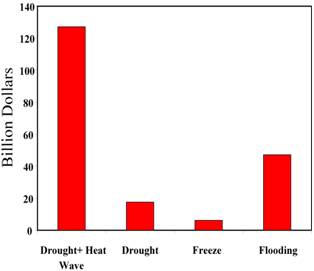
A number of studies have examined the effects of a combination of drought and heat stress on the growth and productivity of maize, barley, sorghum, and different grasses. A combination of drought and heat stress had a significantly higher detrimental effect on the growth and productivity of these plants and crops compared to each of the different stresses applied individually.. A sum of all billion+ dollar US weather disasters between 1980 and 2004 reveals that a combination of drought and heat stress caused an excess of 120 billion dollars in damages. In contrast, over the same period, drought, not accompanied by heat stress, caused some 20 billion dollars in damages (Fig. 2).



